|
|
|
Jordan
![]()

Geography
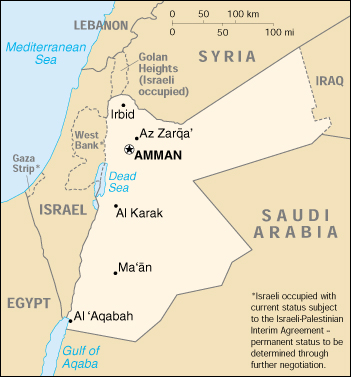
Location: Middle East, northwest of Saudi Arabia
Geographic coordinates: 31 00 N, 36 00 E
Map references: Middle East
Area:
total: 89,213 sq km
land: 88,884 sq km
water: 329 sq km
Area—comparative: slightly smaller than Indiana
Land boundaries:
total: 1,619 km
border countries: Iraq 181 km, Israel 238 km, Saudi Arabia 728 km, Syria 375 km, West Bank 97 km
Coastline: 26 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 3 nm
Climate: mostly arid desert; rainy season in west (November to April)
Terrain: mostly desert plateau in east, highland area in west; Great Rift Valley separates East and West Banks of the Jordan River
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Dead Sea -408 m
highest point: Jabal Ram 1,754 m
Natural resources: phosphates, potash, shale oil
Land use:
arable land: 4%
permanent crops: 1%
permanent pastures: 9%
forests and woodland: 1%
other: 85% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 630 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: NA
Environment—current issues: limited natural fresh water resources; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification
Environment—international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
People
Population: 4,561,147 (July 1999 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 43% (male 1,005,211; female 954,968)
15-64 years: 54% (male 1,265,116; female 1,200,372)
65 years and over: 3% (male 67,852; female 67,628) (1999 est.)
Population growth rate: 3.05% (1999 est.)
Birth rate: 34.31 births/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Death rate: 3.85 deaths/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1 male(s)/female
total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (1999 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 32.7 deaths/1,000 live births (1999 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 73.06 years
male: 71.15 years
female: 75.08 years (1999 est.)
Total fertility rate: 4.64 children born/woman (1999 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Jordanian(s)
adjective: Jordanian
Ethnic groups: Arab 98%, Circassian 1%, Armenian 1%
Religions: Sunni Muslim 96%, Christian 4% (1997 est.)
Languages: Arabic (official), English widely understood among upper and middle classes
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 86.6%
male: 93.4%
female: 79.4% (1995 est.)
Government
Country name:
conventional long form: Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
conventional short form: Jordan
local long form: Al Mamlakah al Urduniyah al Hashimiyah
local short form: Al Urdun
former: Transjordan
Data code: JO
Government type: constitutional monarchy
Capital: Amman
Administrative divisions: 12 governorates (muhafazat, singular—muhafazah); Ajlun, Al 'Aqabah, Al Balqa', Al Karak, Al Mafraq, 'Amman, At Tafilah, Az Zarqa', Irbid, Jarash, Ma'an, Madaba
Independence: 25 May 1946 (from League of Nations mandate under British administration)
National holiday: Independence Day, 25 May (1946)
Constitution: 8 January 1952
Legal system: based on Islamic law and French codes; judicial review of legislative acts in a specially provided High Tribunal; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage: 20 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: King ABDULLAH II (since 7 February 1999)
head of government: Prime Minister Fayez TARAWNEH (since 20 August 1998)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister in consultation with the monarch
elections: none; the monarch is hereditary; prime minister appointed by the monarch
Legislative branch: bicameral National Assembly or Majlis al-'Umma consists of the Senate (a 40-member body appointed by the monarch from designated categories of public figures; members serve four-year terms) and the House of Representatives (80 seats; members elected by popular vote on the basis of proportional representation to serve four-year terms)
elections: House of Representatives—last held 4 November 1997 (next to be held NA November 2001)
election results: House of Representatives—percent of vote by party—NA; seats by party—National Constitutional Party 2, Arab Land Party 1, independents 75, other 2
note: the House of Representatives has been convened and dissolved by the monarch several times since 1974; in November 1989 the first parliamentary elections in 22 years were held
Judicial branch: Court of Cassation
Political parties and leaders: Al-Ahrar (Freedom) Party [Dr. Ahmad ZO'BI, secretary general]; Arab Ba'th Progressive Party [Mahmoud al-MA'AYTAH, secretary general]; Arab Islamic Democratic Party (Doa'a) [Yousif ABU BAKR, secretary general]; Arab Jordanian Ansar Party [Muhammad MAJALI, secretary general]; Arab Land Party [Dr. Muhammad al-'ORAN, secretary general]; Democratic Party of the Left [Musa MA'AITAH, secretary general]; Islamic Action Front [Dr. Ishaq al-FARHAN, secretary general]; Jordanian Arab Constitutional Front Party [Milhem TELL, secretary general]; Jordanian Ba'th Arab Socialist Party [Tayseer al-HOMSI, secretary general]; Jordanian Communist Party [Ya'acoub ZAYADIN, secretary general]; Jordanian Democratic Popular Unity Party [Sa'eed MUSTAPHA, secretary general]; Jordanian Labor Party [Muhammad KHATAYIBAH, secretary general]; Jordanian Peace Party [Dr. Shaher KHREIS, secretary general]; Jordanian People's Democratic Party or HASHD [Salem NAHHAS, secretary general]; Al-Mustaqbal (Future) Party [Suleiman 'ARAR, secretary general]; National Action Party or Haqq [Muhammad ZO'BI, secretary general]; National Constitutional Party [Abdul Hadi MAJALI, secretary general]; National Democratic Public Movement Party [Muhammad al-'AMER, secretary general]; Progressive Party [Na'el BARAKAT, secretary general]; Al-Umma (Nation) Party [Ahmad HNEIDI, secretary general]
International organization participation: ABEDA, ACC, AFESD, AL, AMF, CAEU, CCC, ESCWA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO (correspondent), ITU, MONUA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIBH, UNMOP, UNMOT, UNOMIG, UNPREDEP, UNRWA, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO (applicant)
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Marwan Jamil MUASHIR
chancery: 3504 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 966-2664
FAX: [1] (202) 966-3110
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador William BURNS
embassy: Jabel Amman, Amman
mailing address: P. O. Box 354, Amman 11118 Jordan; APO AE 09892-0200
telephone: [962] (6) 5920101
FAX: [962] (6) 5927712
Flag description: three equal horizontal bands of black (top), white, and green with a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side bearing a small white seven-pointed star; the seven points on the star represent the seven fundamental laws of the Koran
Economy
Economy—overview: Jordan is a small Arab country with inadequate supplies of water and other natural resources such as oil and coal. Jordan benefited from increased Arab aid during the oil boom of the late 1970s and early 1980s, when its annual real GNP growth averaged more than 10%. In the remainder of the 1980s, however, reductions in both Arab aid and worker remittances slowed real economic growth to an average of roughly 2% per year. Imports—mainly oil, capital goods, consumer durables, and food—outstripped exports, with the difference covered by aid, remittances, and borrowing. In mid-1989, the Jordanian Government began debt-rescheduling negotiations and agreed to implement an IMF-supported program designed to gradually reduce the budget deficit and implement badly needed structural reforms. The Persian Gulf crisis that began in August 1990, however, aggravated Jordan's already serioeconomic problems, forcing the government to shelve the IMF program, stop most debt p, and suspend rescheduling negotiations. Aid from Gulf Arab states, worker remittances, and trade contracted; and refugees flooded the country, producing serious balance-of-payments problems, stunting GDP growth, and straining government resources. The economy rebounded in 1992, largely due to the influx of capital repatriated by workers returning from the Gulf, but recovery was uneven. A preliminary agreement with the IMF in early 1999 will provide new loans over the next three years. Sluggish growth, along with debt, poverty, and unemployment are fundamental ongoing economic problems.
GDP: purchasing power parity—$15.5 billion (1998 est.)
GDP—real growth rate: 2.2% (1998 est.)
GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$3,500 (1998 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
agriculture: 6%
industry: 30%
services: 64% (1995 est.)
Population below poverty line: 30% (1998 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 2.4%
highest 10%: 34.7% (1991)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 4% (1998 est.)
Labor force: 1.15 million
note: in addition, there are 300,000 foreign workers (1997 est.)
Labor force—by occupation: industry 11.4%, commerce, restaurants, and hotels 10.5%, construction 10%, transport and communications 8.7%, agriculture 7.4%, other services 52% (1992)
Unemployment rate: 15% official rate; note—actual rate is 25%-30% (1998 est.)
Budget:
revenues: $2.8 billion
expenditures: $3 billion, including capital expenditures of $672 million (1999 est.)
Industries: phosphate mining, petroleum refining, cement, potash, light manufacturing
Industrial production growth rate: -3.4% (1996)
Electricity—production: 5.52 billion kWh (1996)
Electricity—production by source:
fossil fuel: 99.64%
hydro: 0.36%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1996)
Electricity—consumption: 5.52 billion kWh (1996)
Electricity—exports: 0 kWh (1996)
Electricity—imports: 0 kWh (1996)
Agriculture—products: wheat, barley, citrus, tomatoes, melons, olives; sheep, goats, poultry
Exports: $1.5 billion (f.o.b., 1997 est.)
Exports—commodities: phosphates, fertilizers, potash, agricultural products, manufactures
Exports—partners: Iraq, India, Saudi Arabia, EU, Indonesia, UAE, Syria, Ethiopia
Imports: $3.9 billion (c.i.f., 1997 est.)
Imports—commodities: crude oil, machinery, transport equipment, food, live animals, manufactured goods
Imports—partners: EU, Iraq, US, Japan, Turkey, Malaysia, Syria, China
Debt—external: $7.5 billion (1998 est.)
Economic aid—recipient: $1.097 billion (1995); note—received $320 million from ODA in 1998 (est.)
Currency: 1 Jordanian dinar (JD) = 1,000 fils
Exchange rates: Jordanian dinars (JD) per US$1—0.7090 (January 1999-1996), 0.7005 (1995), 0.6987 (1994), 0.6928 (1993)
note: since May 1989, the dinar has been pegged to a basket of currencies
Fiscal year: calendar year
Communications
Telephones: 425,000 (1998)
Telephone system:
domestic: microwave radio relay, coaxial and fiber-optic cable, and cellular; Jordan has two cellular telephone providers (with approximately 50,000 subscribers in 1998), ten data service providers, and four Internet service providers (with approximately 8,000 subscribers in 1998)
international: satellite earth stations—3 Intelsat, 1 Arabsat, and 29 land and maritime Inmarsat terminals (1996); coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, and microwave radio relay to Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Syria, and Israel; building a Red Sea Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) fiber-optic submarine cable link and planning to update links with Saudi Arabia and Israel to fiber-optic cable; 4,000 international circuits (1998 est.); participant in Medarabtel
Radio broadcast stations: AM 6, FM 7, shortwave 1 (1998 est.)
Radios: 1.1 million (1992 est.)
Television broadcast stations: 8 (in addition, there are approximately 42 repeaters and 1 TV receive-only satellite link) (1997)
Televisions: 350,000 (1992 est.)
Transportation
Railways:
total: 677 km
narrow gauge: 677 km 1.050-m gauge; note—an additional 110 km stretch of the old Hejaz railroad is out of use (1998 est.)
Highways:
total: 8,000 km
paved: 8,000 km
unpaved: 0 km (1998 est.)
Pipelines: crude oil 209 km
Ports and harbors: Al 'Aqabah
Merchant marine:
total: 7 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 42,746 GRT/59,100 DWT
ships by type: bulk 2, cargo 2, container 1, livestock carrier 1, roll-on/roll-off cargo 1 (1998 est.)
Airports: 17 (1998 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
total: 14
over 3,047 m: 9
2,438 to 3,047 m: 4
under 914 m: 1 (1998 est.)
Airports—with unpaved runways:
total: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 2 (1998 est.)
Military
Military branches: Jordanian Armed Forces (JAF; includes Royal Jordanian Land Force, Royal Naval Force, and Royal Jordanian Air Force); Badiya (irregular) Border Guards; Ministry of the Interior's Public Security Force (falls under JAF only in wartime or crisis situations)
Military manpower—military age: 18 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
males age 15-49: 1,113,998 (1999 est.)
Military manpower—fit for military service:
males age 15-49: 793,002 (1999 est.)
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
males: 49,954 (1999 est.)
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $608.9 million (FY 98)
Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 7.8% (1997)